Purchasing a used hybrid battery can save you thousands of dollars, but only if you know what you’re getting. The global market for second-hand hybrid batteries continues to grow as more drivers in the Middle East and South Asia seek affordable alternatives to expensive OEM replacements. Whether you plan to install a pre-owned battery in your vehicle or sell your old unit to a recycling centre, understanding battery health is essential for making informed decisions.
This comprehensive guide walks you through professional testing methods, warning signs to watch for, and how recycling centres like Recohub evaluate batteries they receive. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the used hybrid battery market.
Why Does Hybrid Battery Testing Matter?
Testing matters because hybrid batteries degrade gradually, and visible condition rarely tells the full story. A battery pack might look perfectly clean on the outside while harbouring weak cells that dramatically reduce performance and lifespan.
According to research published by the U.S. Department of Energy, proper battery management through testing and monitoring can extend battery life by up to 30%. This significant improvement demonstrates why investing time in thorough evaluation pays dividends. For buyers, testing reveals the true value of what they’re purchasing. For sellers looking to trade in their batteries at facilities like Recohub, understanding health metrics helps set realistic expectations and ensures fair compensation.
The hybrid battery price you receive or pay depends heavily on documented health status. Centres that purchase used batteries for recycling or refurbishment base their offers on measurable capacity, cell balance, and overall condition. Knowing these numbers before any transaction puts you in a stronger negotiating position.
What Types of Batteries Power Hybrid Vehicles?
Two main battery technologies dominate the hybrid vehicle market today. The nickel metal hydride battery remains popular in many Toyota, Honda, and Suzuki models due to its proven reliability and excellent thermal stability. Meanwhile, lithium-ion batteries have gained ground in newer vehicles thanks to their higher energy density and lighter weight.
Research from ScienceDirect indicates that nickel metal hydride batteries can withstand more than 12,000 charge cycles with less than 5% capacity loss under optimal conditions. This durability explains why manufacturers like Toyota continued using this technology in hybrid models for decades. The chemistry proves particularly forgiving of temperature extremes and overcharging, making it ideal for regions with hot climates common throughout the Middle East and South Asia.
Lithium-ion variants offer advantages in weight and efficiency but require more sophisticated battery management systems. Both technologies have active secondary markets, and recycling centres accept either type for material recovery or refurbishment.
How Long Should a Hybrid Battery Last?
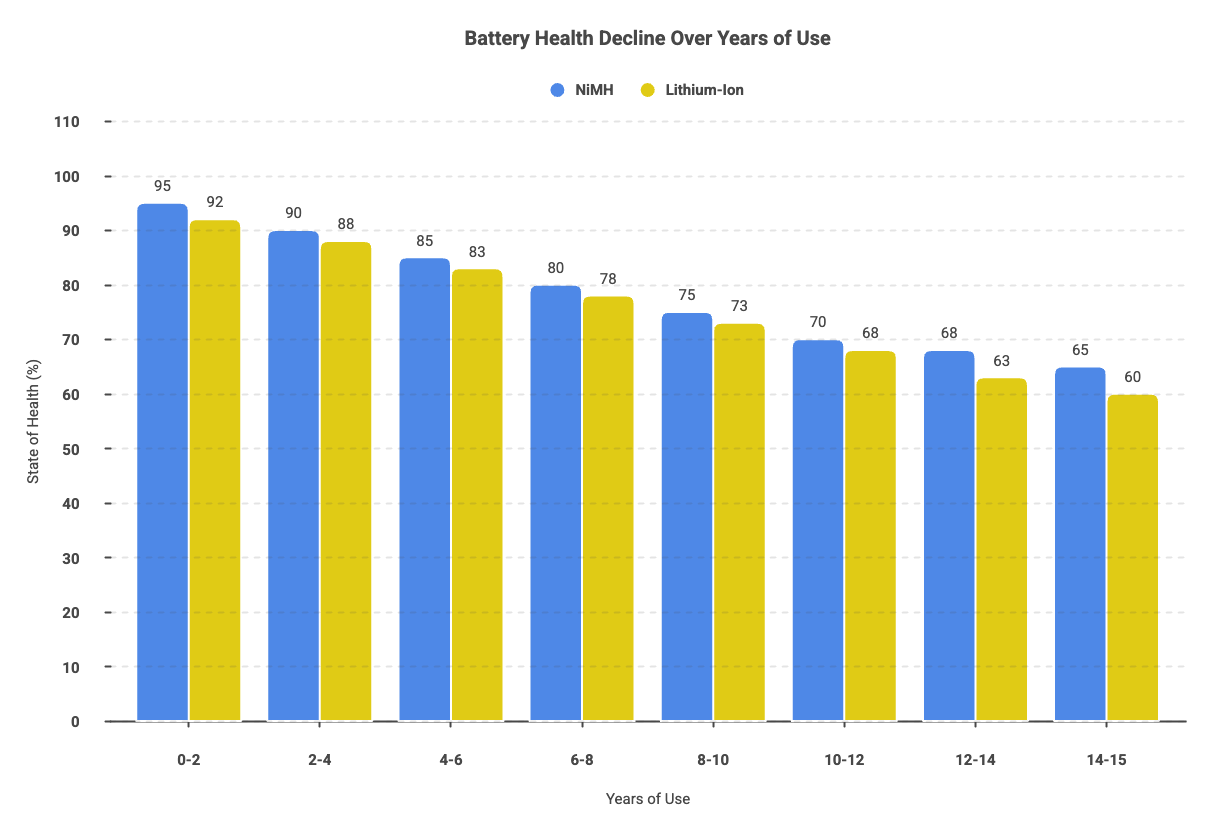
Most hybrid batteries deliver reliable service for 8 to 15 years or between 100,000 and 200,000 kilometres, depending on usage patterns and maintenance. This range varies based on driving conditions, climate, charging habits, and the specific battery technology employed.
Factors that accelerate degradation include frequent short trips that prevent full charge cycles, extreme temperature exposure, and aggressive driving that demands high power output. Conversely, batteries in vehicles used for steady highway driving often exceed expected lifespans.
The Ertiga hybrid battery price and value, for example, depends partly on age but more significantly on actual state of health. A five-year-old battery with excellent cell balance could outperform a two-year-old unit that has suffered heat damage or improper storage.
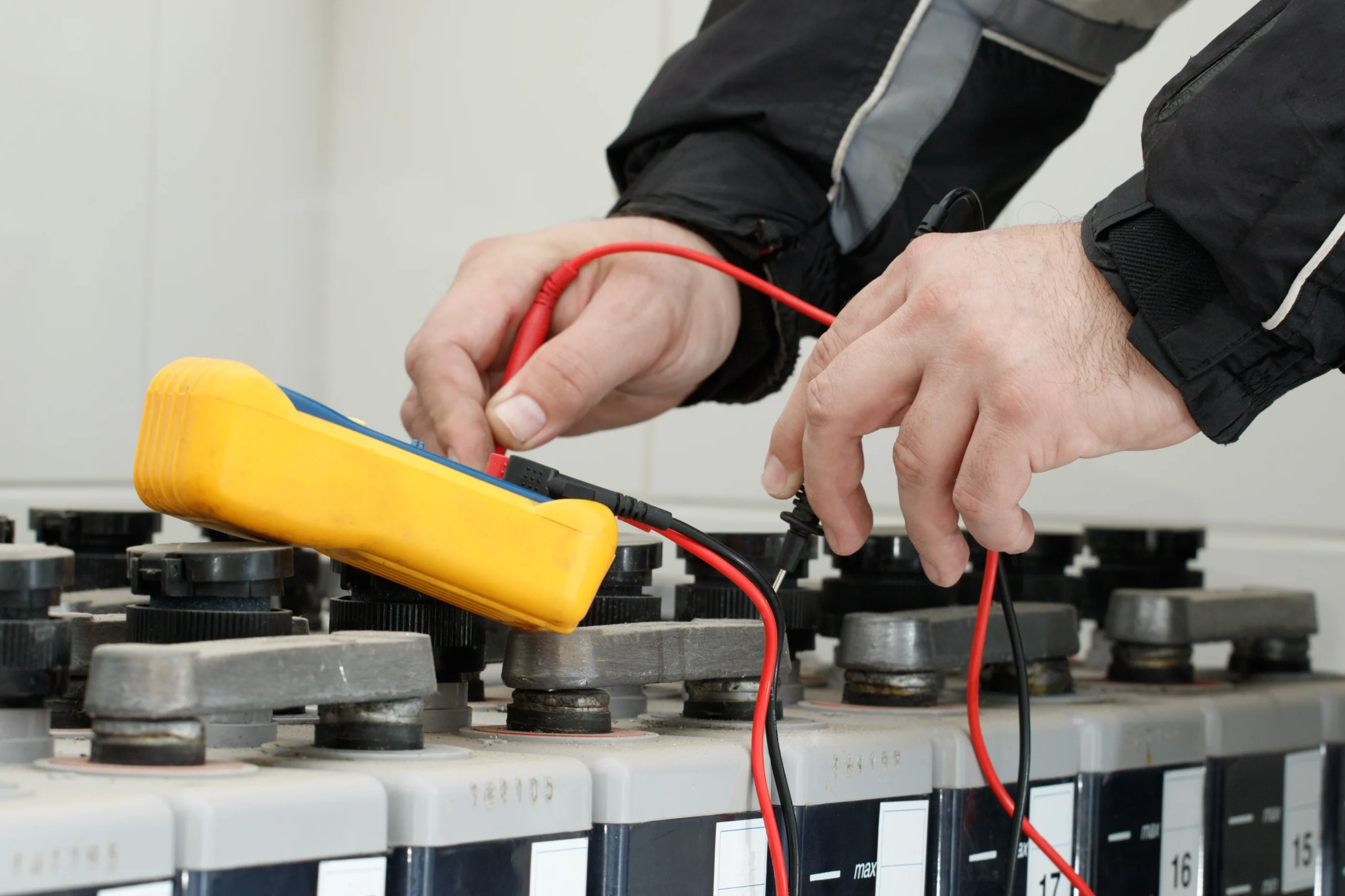
Professional Testing Methods for Hybrid Batteries
OBD-II Diagnostics and Trouble Code Analysis
The on-board diagnostic port provides direct access to battery management system data. Professional scan tools retrieve trouble codes, live voltage readings, and state of charge information. Apps like Dr. Prius and Dr. Hybrid work with Bluetooth OBD readers to display battery health metrics on smartphones, making basic diagnostics accessible to non-professionals.
Key parameters to examine include individual cell voltages, temperature differentials across the pack, and any stored fault codes. Healthy cells typically maintain voltages between 7.2 and 8.4 volts for nickel metal hydride units. Significant variation between cells indicates imbalance that requires attention.
Load Testing and Stress Analysis
Load testing applies controlled electrical demand to the battery while monitoring response. This method reveals how well the pack handles real-world conditions that static voltage measurements cannot capture. Technicians observe voltage drop under load, recovery time after discharge, and heat generation during the test.
A common approach involves putting the vehicle in reverse, engaging the electric motor while holding the brakes, and watching how quickly minimum and maximum cell voltages diverge. New or healthy batteries maintain tight voltage spread, while degraded packs show widening gaps that indicate failing cells.
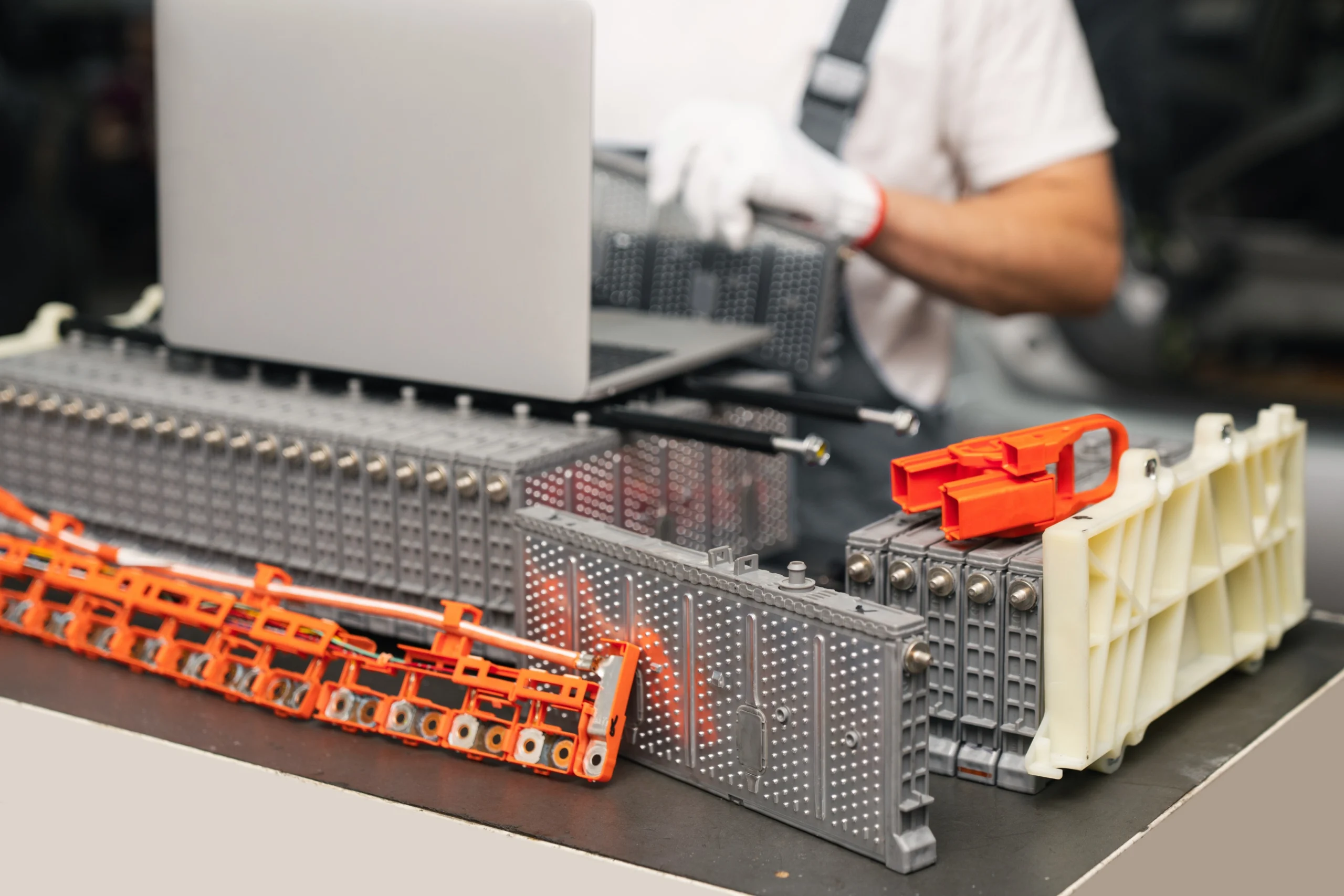
Capacity Testing and State of Health Calculation
State of health represents remaining capacity compared to original specifications. Professional equipment measures actual amp-hour capacity through controlled discharge cycles. Results appear as percentages, with anything above 70% generally considered serviceable for continued use.
Battery recycling centres like Recohub perform these assessments on incoming batteries to determine appropriate handling. Units with sufficient remaining capacity may qualify for refurbishment and resale, while those below threshold proceed to material recovery. Understanding these categories helps sellers anticipate how their batteries will be evaluated.
Battery Health Indicators at a Glance
The following table summarises key metrics and their implications for battery condition:
Health Indicator | Good Condition | Fair Condition | Poor Condition |
State of Health (SOH) | Above 80% | 60-80% | Below 60% |
Cell Voltage Spread | Under 0.3V | 0.3V – 1.0V | Over 1.2V |
Internal Resistance | Uniform across cells | Minor variations | Significant outliers |
Trouble Codes | None present | Historical codes cleared | Active P3000-series codes |
Resale/Recycling Value | Highest | Moderate | Recycling value only |
Warning Signs of a Failing Hybrid Battery
Several symptoms indicate battery problems that testing will confirm. Dashboard warning lights, particularly the master warning and check hybrid system alerts, demand immediate attention. These indicators often appear before complete failure, providing opportunity for proactive response.
Decreased fuel economy represents another common sign. Hybrid systems depend on battery-powered electric assistance during acceleration and low-speed operation. When battery capacity drops, the petrol engine must work harder, consuming more fuel. Drivers who notice sudden changes in consumption should investigate battery health.
Erratic battery gauge behaviour, reduced electric-only range, unusual noises from the battery cooling fan, and sluggish acceleration all warrant testing. Catching these symptoms early maximises options, whether that means repair, replacement, or selling the battery to a recycling facility before further degradation reduces its value.
Selling Your Used Hybrid Battery to Recycling Centres
When your hybrid battery no longer meets your needs, responsible disposal through certified recycling centres offers environmental and financial benefits. Facilities across the Middle East and South Asia accept used batteries for processing, recovering valuable materials like nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements.
Recohub operates collection centres that evaluate incoming batteries and provide fair compensation based on documented condition. The evaluation process examines the same health metrics discussed throughout this guide, making pre-testing valuable for setting expectations. Batteries with higher remaining capacity command better prices, while severely degraded units still hold value for material recovery.
For detailed information about how recycling centres process hybrid batteries and what to expect when you bring yours in, read our comprehensive guide on hybrid battery recycling processes and local collection options.
Can You Test a Hybrid Battery Yourself?
Yes, basic testing is possible with consumer-grade equipment, though professional assessment provides more comprehensive results. Bluetooth OBD-II adapters combined with dedicated hybrid diagnostic apps allow monitoring of cell voltages, temperature readings, and fault codes from your smartphone.
Safety considerations matter significantly with high-voltage battery systems. Hybrid battery packs operate at voltages between 200 and 350 volts, requiring respect and appropriate precautions. Never attempt to open battery enclosures or directly contact terminals without proper training and equipment. Basic OBD diagnostics pose no safety concerns since they only read data from the vehicle’s computer systems.
Professional testing adds value when buying or selling batteries because certified results carry more weight. Independent shops with hybrid expertise and manufacturer dealerships both offer testing services. The investment in professional assessment often pays for itself through better negotiating position or avoided problems.
Making Informed Decisions About Hybrid Batteries
Whether buying a used battery to extend your vehicle’s life or selling one that has served its purpose, knowledge about health testing empowers better decisions. The methods described here, from basic OBD diagnostics to professional capacity testing, reveal the true condition behind any hybrid battery’s appearance.
The growing network of recycling facilities across the Middle East and South Asia means convenient options exist for responsible battery disposal. Centres like Recohub offer straightforward evaluation and fair compensation, turning end-of-life batteries into valuable resources rather than waste. Test before you buy, document condition before you sell, and contribute to the circular economy that makes hybrid technology sustainable for future generations.
FAQ
How much does a hybrid battery health check cost?
Professional hybrid battery testing typically costs between $50 and $150, depending on the depth of analysis. Basic OBD scans fall at the lower end, while comprehensive capacity testing with detailed reports costs more. Many recycling centres offer free evaluations when you bring your battery for assessment or sale.
What is the average hybrid battery price for replacement in 2026?
New OEM hybrid batteries range from $2,000 to $8,000 depending on vehicle make and model. Refurbished batteries offer savings of 30-50%, typically costing $1,500 to $4,000. The hybrid battery price you pay depends on whether you choose new, refurbished, or remanufactured options.
Can I sell my old nickel metal hydride battery for recycling?
Yes, recycling centres actively purchase used nickel metal hydride battery packs because they contain valuable recoverable materials. Facilities like Recohub accept batteries regardless of condition, though units with higher remaining capacity command better prices. Contact your nearest centre for current rates and collection arrangements.
How do I know if my hybrid battery is still under warranty?
Most manufacturers offer 8 to 10-year warranties on hybrid battery packs, with some extending coverage to 150,000 miles. Check your vehicle’s original purchase documentation or contact an authorised dealer with your VIN number. Warranty claims require documented failure rather than gradual capacity loss, making independent testing valuable for understanding your specific situation.
Where can I recycle hybrid batteries in the Middle East and South Asia?
Certified recycling centres operate throughout both regions, with Recohub maintaining collection points for convenient drop-off. Many centres also arrange pickup services for larger quantities. Responsible recycling ensures proper handling of hazardous materials while recovering valuable metals for reuse in new battery production.